14 KiB
+++ title="We tried IPFS over Garage" date=2022-06-09 +++
Once you have spawned your Garage cluster, you might want to federate or share efficiently your content with the rest of the world. In this blog post, we try to connect the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) daemon to Garage. We discuss the different bottleneck and limitations of the currently available software.
Some context
People often struggle to see the difference between IPFS and Garage, so let's start by making clear that these projects are complementary and not interchangeable.
Personnaly, I see IPFS as the intersection between Bittorrent and a filesystem. Bittorrent remains probably one of the most efficient way to deliver a copy of a file or a folder to a very large number of people. But it lacks some interactivity: once a torrent file has been generated, you can't simply add a file to it. By adopting a filesystem abstraction, IPFS handles such use case smoothly.
However, you would probably not rely on Bittorrent to durably store your encrypted holiday pictures you shared with your friends, and this is the same for IPFS. If at some time, everyone has a copy of the picture on their hard disk, people might delete it after a while without you knowing it. You also can't easily collaborate to share this common treasure, for example, there is no automatic way to say that Alice and Bob are in charge of storing the first half of the archive while Charlie and Eve are in charge of the second half.
➡️ IPFS is designed to deliver content.
Note: the IPFS project has another project named IPFS Cluster that allow servers to collaborate on hosting IPFS content. The Bittorrent project created Bittorrent Sync, renamed later Resilio, that provide a filesystem abstraction based on the Bittorrent protocol. Reviewing these solutions is out of the scope of this article, feel free to try them by yourself!
Garage, on the contrary, is designed to spread automatically your content over all your available nodes to optimize your storage space. At the same time, it ensures that your content is always replicated exactly 3 times across the cluster (or less if you change a configuration parameter!) on different geographical zones (if possible).
But independant Garage nodes can not collaborate to deliver popular contents: every one is playing alone. All ressources created (keys, files, buckets) are tightly coupled to a cluster, people from different clusters can't collaborate on the same data (without additional software).
➡️ Garage is designed to durably store content.
In this blog post, we will explore if we can combine both properties by connecting an IPFS node to a Garage cluster.
Try #1: Vanilla IPFS over Garage
IPFS is available as a pre-compiled binary. But to connect it with Garage, we need a plugin named ipfs/go-ds-s3. The Peergos project has a fork because it seems that the plugin is notorious for hitting Amazon's rate limits #105, #205. This is the one we will try in the following.
The easiest solution to use this plugin in IPFS is to bundle it in the main IPFS daemon, and thus recompile IPFS from source. Following the instructions on the README file allowed me to spawn an IPFS daemon configured with S3 as the block store.
Just be careful when adding the plugin to the plugin/loader/preload_list file, the given command lacks a newline.
You must edit the file manually after running it, you will directly see the problem and be able to fix it.
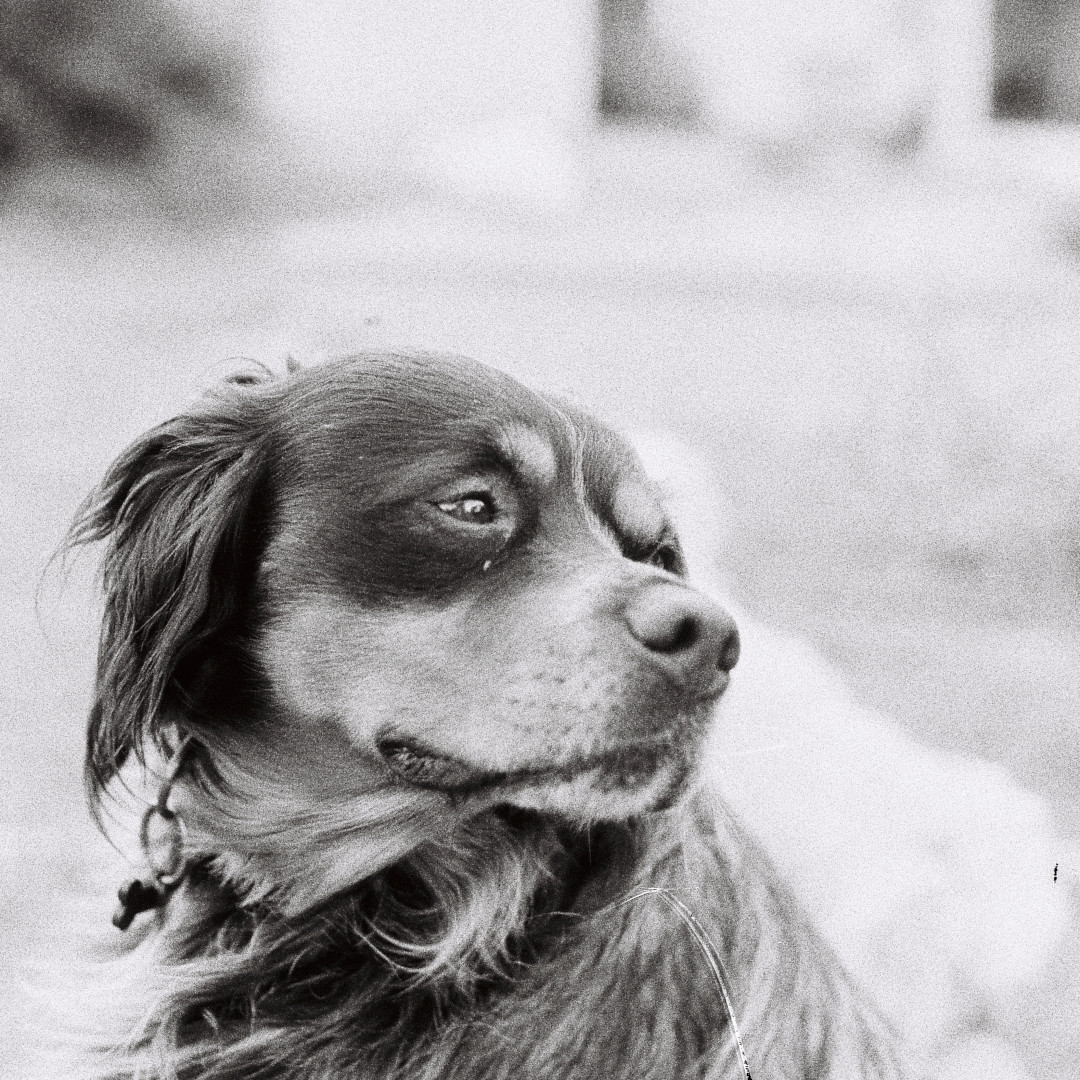
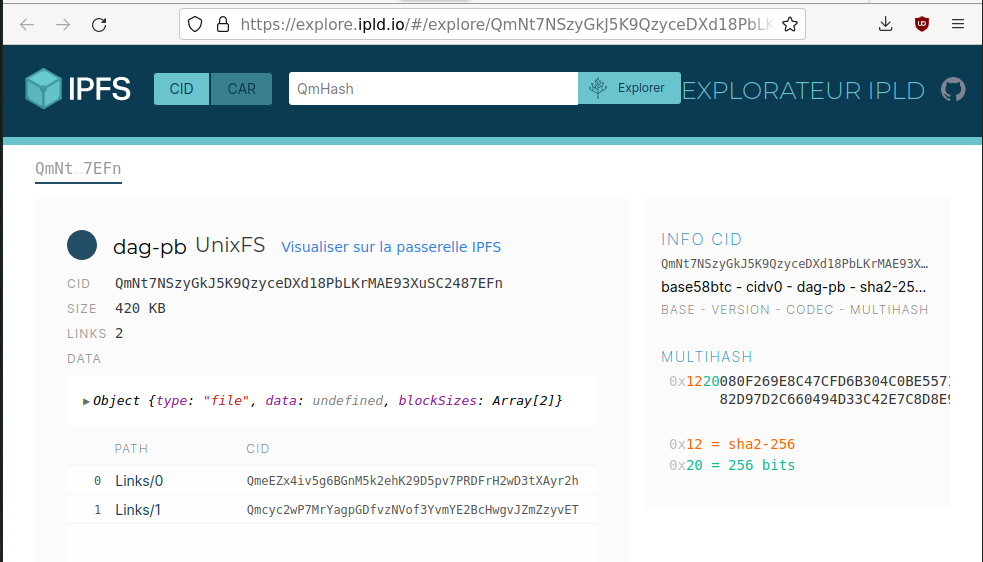
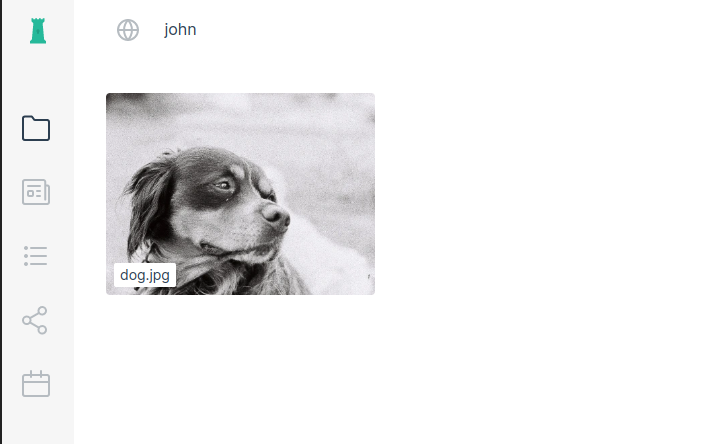
After that, I just ran the daemon and accessed the web interface to upload a photo of my dog:
The photo is assigned a content identifier (CID):
QmNt7NSzyGkJ5K9QzyceDXd18PbLKrMAE93XuSC2487EFn
And it now accessible on the whole network. You can inspect it from the official gateway for example:
At the same time, I was monitoring Garage (through the OpenTelemetry stack we have implemented earlier this year). Just after launching the daemon and before doing anything, we have this surprisingly active Grafana plot:
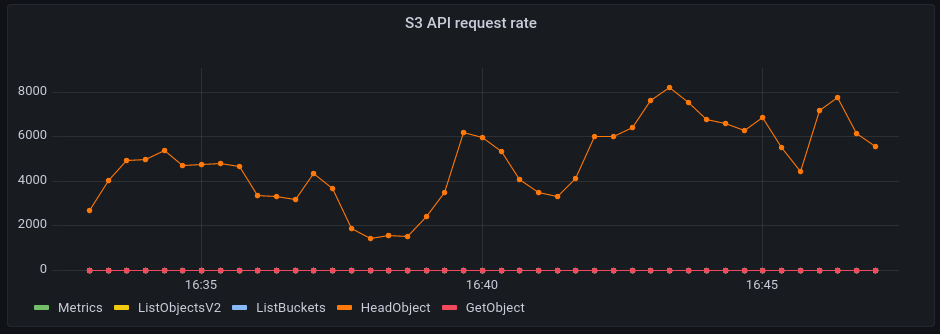 Legend: y axis = requests per 10 seconds, x axis = time
Legend: y axis = requests per 10 seconds, x axis = time
It means that in average, we have around 250 requests per second, mainly to check that an IPFS block does not exist locally. These requests are triggered by the DHT service of IPFS: my node being reachable over the Internet, it acts as a public DHT server and start answering global block requests over the whole network. Each time it sees a block request, it sends a request to our backend to see if it exists.
We will try to tweak the IPFS configuration later - we know that we can deactivate the DHT server. For now, we will continue with the default parameters.
When I start interacting with IPFS by sending a file or browsing the default proposed catalogs (ie. the full XKCD archive), values become so high that our default OpenTelemetry configuration can not cope with them. We have the following error in Garage's logs:
OpenTelemetry trace error occurred. cannot send span to the batch span processor because the channel is full
It is useless to change Garage parameters to see what is exactly the number of requests done on the cluster: it is way too high considering my targeted usage: sharing a picture. As a comparison, this whole webpage, with its pictures, triggers around 10 requests on Garage to load, not thousands.
I think we can conclude that this first try was a failure. The S3 datastore on IPFS does too many request and would need some important work to optimize it. But we should not give up too fast, because Peergos folks are known to run their software based on IPFS, in production, with an S3 backend.
Try #2: Peergos over Garage
Peergos is designed as an end-to-end encrypted and federated alternative to Nextcloud. Internally, it is built upon IPFS and is known to have a deep integration of the S3 API One important point of this integration is that your browser is able to bypass both the Peergos daemon and the IPFS daemon to write and read IPFS blocks directly on the backemd.
I don't know exactly if Peergos is still considered in alpha or switched to beta, but keep in mind that it might be more experimental that you would like!
Starting Peergos on top of Garage required some small patches on both sides, but in the end, we were able to get it working. I was able to upload my file, see it in the interface, create a link to share it, rename it, move it in a folder, and so on:
At the same time, the fans of my computer started to become a bit loud. A quick look at Grafana shows that Garage is still very busy.
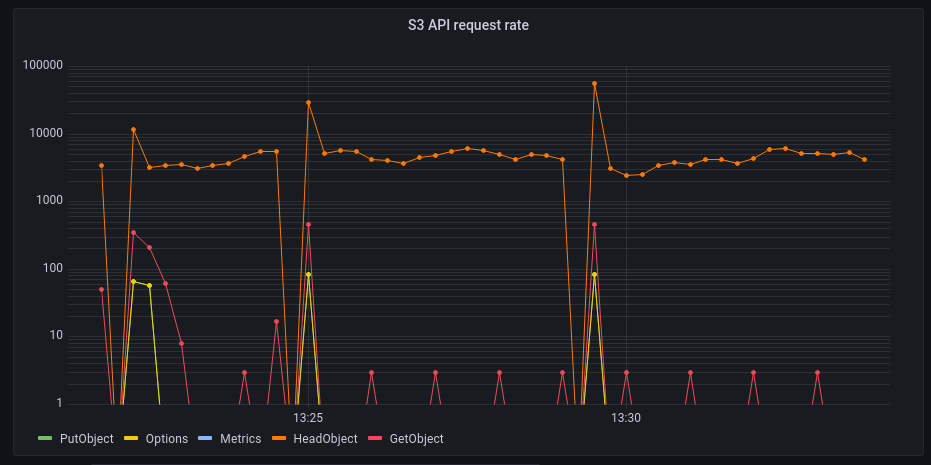 Legend: y axis = requests per 10 seconds on log(10) scale, x axis = time
Legend: y axis = requests per 10 seconds on log(10) scale, x axis = time
Again, the workload is dominated by the HeadObject requests.
After getting a look at ~/.peergos/.ipfs/config, it seems the IPFS configuration used by the Peergos project is pretty standard.
And thus, again, we are acting as a DHT server, answering each second to thousands of block requests.
We also some traffic on the GetObject endpoints (peaks of ~45 req/sec) and the OPTIONS HTTP verb.
This is the traffic generated by Peergos. The OPTIONS HTTP verb is here because we use the direct access feature of Peergos: our browser is sending CORS requests to Garage.
Internally, IPFS splits files in blocks of less than 256 kB, my picture is thus split in 2 blocks, requiring 2 requests over Garage to fetch it.
But even by knowing that IPFS split files in small blocks, I can't explain why we have so much GetObject requests.
Try #3: Optimizing IPFS
We have seen in our 2 precedent tries that the main source of load was the federation, and more especially, the DHT server. In this section, we want to artificially remove this problem of the equation by preventing our IPFS node from federating and see what pressure is put by Peergos alone on our local cluster.
To isolate IPFS, we have set its routing type to none, we have cleared its bootstrap node list,
and we configured the swarm socket to listen only on localhost.
Finally, we restart Peergos and observe this more peaceful graph:
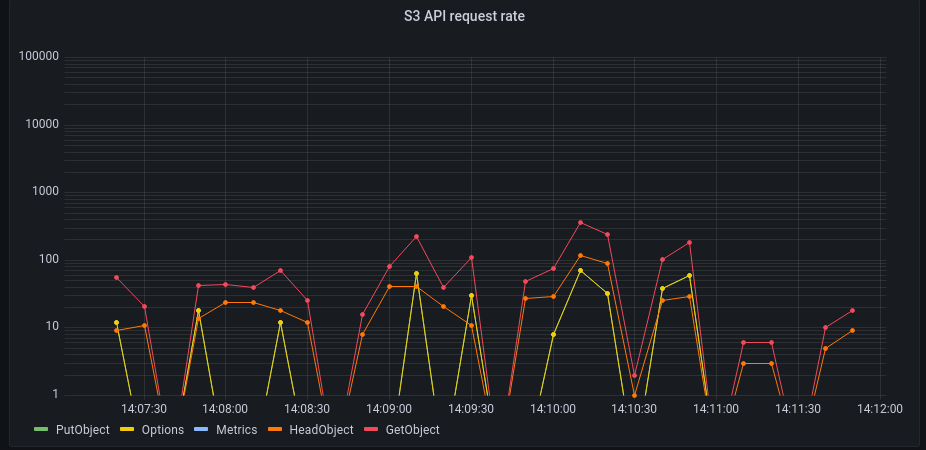 Legend: y axis = requests per 10 seconds on log(10) scale, x axis = time
Legend: y axis = requests per 10 seconds on log(10) scale, x axis = time
Now, for a given endpoint, we have peaks of around 10 req/sec which is way more reasonable. Furthermore, we are not hammering anymore our backend with requests on objects that are not here.
The next step would be to gradually allowing back our node to connect to the IPFS network,
while ensuring that the traffic to the S3 cluster remains low. For example, configuring our IPFS
node as a dhtclient instead of dhtserver would exempt it from answering public DHT requests.
Keeping an in-memory index (as a hashmap and/or blum filter) of the blocks stored on the current node
could also drastically reduce the number of requests.
It could also be interesting to explore ways to run in one process a full IPFS node with a DHT
server on the regularer filesystem datastore, and reserve a second process configured with the S3 datastore
to handle only our Peergos data.
However, with these optimizations, the best we can expect is the traffic we have on the previous plot. From a theoretical perspective, it is still higher than the optimal number of requests. On S3, storing a file, downloading a file, listing available files are all actions that can be done in a single request. Even if all requests have not the same cost on the cluster, processing a request has a non neglictible fixed cost.
S3 and IPFS are incompatible?
Text by Alex
Conclusion
Running IPFS over a S3 backend does not quite work out of the box in term of performances yet. We have identified that the main problem is linked with the DHT service, and proposed some improvements (disabling the DHT server, keeping an in-memory index of the blocks, using the S3 backend only for your data).
From a design perspective, it seems however that the numerous small blocks created by IPFS do not map trivially to efficient S3 requests, and thus could be a limiting factor to any optimization work.
As part of our test journey, we also read some posts about performance issues on IPFS (eg. #6283) that are not linked with the S3 connector. We might be negatively influenced by our failure to connect IPFS with S3, but we are tempted to think that IPFS is intrinsically ressource intensive.
On our side, we will continue our investigations towards more minimalist software. This choice makes sense for us as we want to reduce the ecological impact of our services by deploying less servers, that use less energy, and that are renewed less frequently.
Yes we are aware of the existence of Nextcloud, Owncloud, Owncloud Infinite Scale, Seafile, Filestash, Pydio, SOLID, Remote Storage, etc. We might even try one of them in a future post, so stay tuned!